SUMMARY: Identification of 2 novel genetic variants associated with an increased risk of developing diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
DESCRIPTION: B-cells are a type of white blood cell that plays an important role in our immune system by producing antibodies that help detect and destroy germs. However, abnormal B-cell growth has the potential to form diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), an aggressive form of cancer. A family history of lymphoma has previously been associated with an increased risk of developing the disease. This study examined over 17,000 individuals of European ancestry to further characterize genetic factors associated with an increased risk of developing the disease. It identified novel 2 variants associated with a risk of developing DLBCL, both of which are located in the proximity of genes that play a role in the immune system.
DID YOU KNOW? DLBCL is exceptionally sensitive to chemotherapy, which is generally used as a first line of treatment. Other treatment avenues include radiation therapy, stem cell transplants, and immunotherapy. [SOURCE]
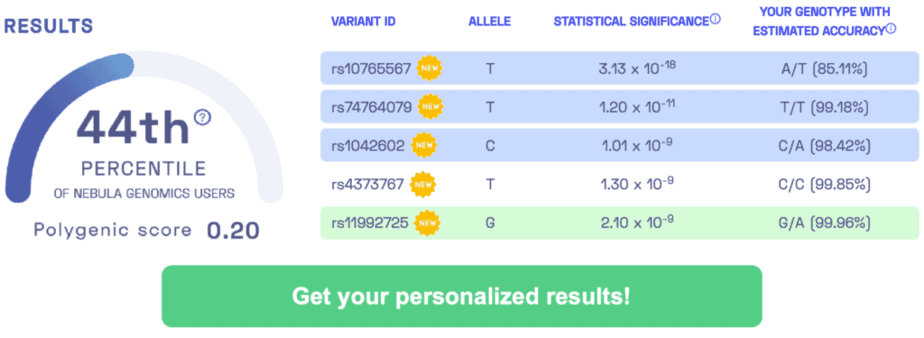
SAMPLE RESULTS: Learn more about the Nebula Research Library.
DLBCL-ASSOCIATED VARIANTS: rs9831894, rs6773363
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES:
B-Cells
What is Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma?
WEEKLY UPDATE: October 17, 2019
