STUDY TITLE: HLA Class II Locus and Susceptibility to Podoconiosis
SUMMARY: Identification of a genomic region associated with susceptibility to developing podoconiosis.
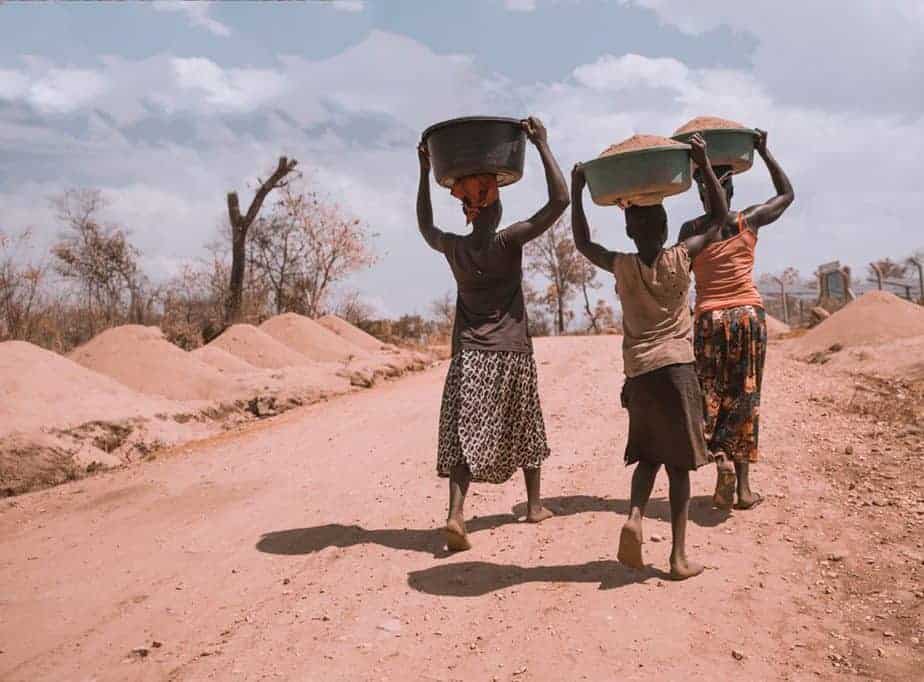
OVERVIEW: Podoconiosis is a disease that many people may have never heard of, yet in some communities across the globe, nearly 1 in 20 individuals are affected. The disease predominantly affects farmers and people that walk barefoot on red-clay soil formed from volcanic rock that is found in tropical Africa, Central and South America, and north India. Scientists think that red-clay soil contains large amounts of minerals which are absorbed through the skin of the feet. This induces a reaction of the immune system that leads to the characteristic swelling of the feet. Genetics is thought to contribute over 60% to a person’s risk of developing podoconiosis. This genome-wide study examined nearly 400 individuals from southern Ethiopia to identify genetic variants associated with podoconiosis, and found a significant association with the HLA-DQA1 region, that has an important function in the immune system.
DID YOU KNOW? The World Health Organization believes that it is possible to eradicate podoconiosis. Efforts to increase the availability of shoes, and the further development of roads, are seen as key strategies to control the disease. [SOURCE]
SAMPLE RESULTS: Learn more about the Nebula Research Library.
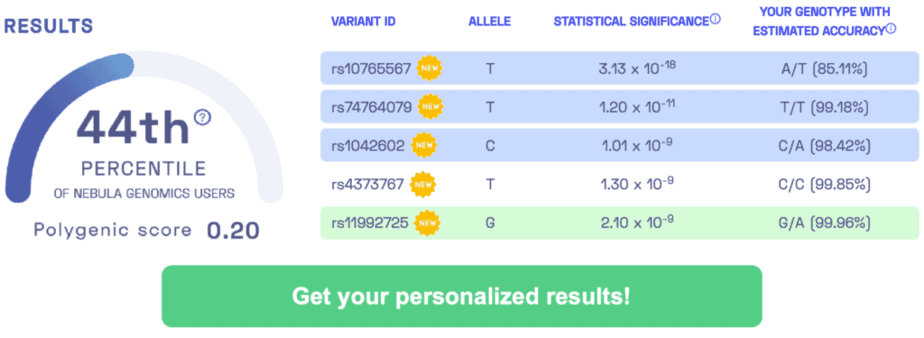
PODOCONIOSIS-ASSOCIATED VARIANTS: rs17612858
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES:
More information on this condition
WEEKLY UPDATE: February 8, 2020
