SUMMARY: Discovery of a variant in the FLT1 gene associated with susceptibility to sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome.
OVERVIEW: Sepsis occurs when chemicals released in the bloodstream to fight an infection trigger inflammation throughout the body. Sepsis can be life-threatening and lead to long-term damage of many organs. If the lungs become affected, it can result in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), whereby fluids enter the lungs, making it extremely difficult to breathe. Individuals who survive ARDS are often left with permanent cognitive and physical impairment that is caused by organ damage due to insufficient oxygen supply. This genome-wide study examined nearly 2,000 individuals of European ancestry to better understand the genetic predisposition to developing ARDS in patients with sepsis. The study discovered one variant in the FLT1 gene. FLT1 encodes a receptor that plays an important role in the development and function of the body’s vasculature.
DID YOU KNOW? Sepsis is estimated to affect nearly 30 million individuals each year. Vulnerable populations include the elderly, pregnant women, and hospitalized patients. [SOURCE]
SAMPLE RESULTS: Learn more about the Nebula Research Library.
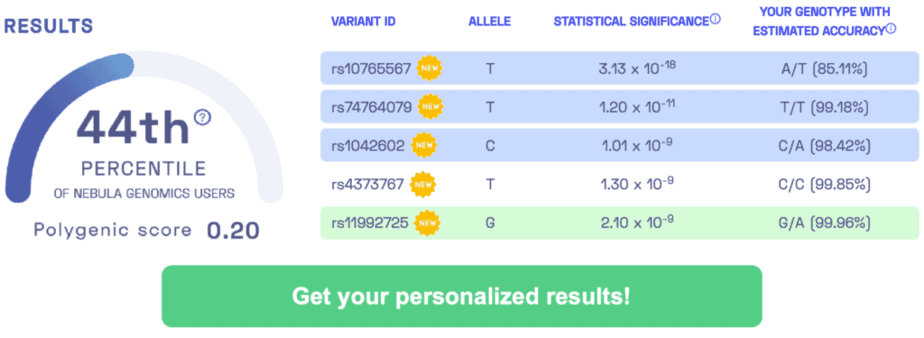
ANALYZED VARIANTS: rs9508032
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES:
What is sepsis? (Video)
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
WEEKLY UPDATE: January 31, 2020