STUDY TITLE: Genetic risk factors for variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease: a genome-wide association study
SUMMARY: Identification of a genetic variant that confers resistance to transmissible Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
OVERVIEW: Prion diseases are brain disorders caused by misfolded proteins that form aggregates leading to progressive, fatal dementia. Some prion diseases are transmissible. For example, consuming meat infected with misfolded prion proteins can induce the body’s own prion proteins to misfold and aggregate. This study examined the genetic information of over 5,000 individuals from the United Kingdom and Papua New Guinea to understand the susceptibility to a transmissible Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD). The study identified one variant allele that confers resistance to infection with the CJD prion protein. This variant allele is located in the human prion gene and prevents induced misfolding and aggregation of the human prion proteins.
DID YOU KNOW? While prion diseases are exceedingly rare, there is currently no cure. The spread of transmissible prion disease must be carefully controlled through the destruction of tainted meat and proper sterilization of medical equipment. [SOURCE]
SAMPLE RESULTS: Learn more about the Nebula Research Library.
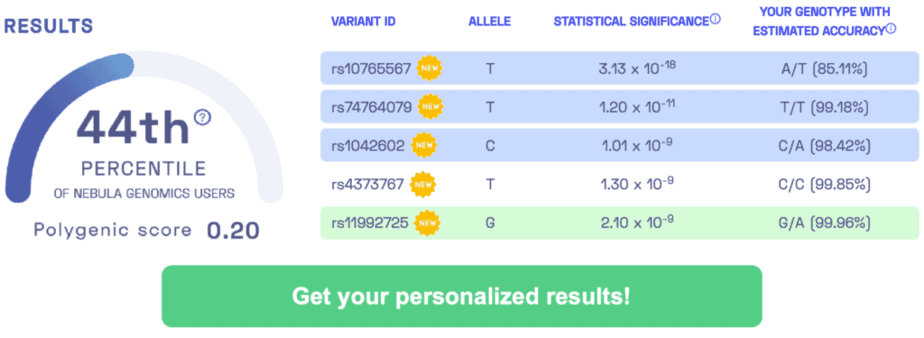
PRION DISEASE-ASSOCIATED VARIANTS: rs1799990
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES:
Prions (Video)
Transmissible Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
WEEKLY UPDATE: December 12, 2019