STUDY TITLE: Genomic analysis of diet composition finds novel loci and associations with health and lifestyle
SUMMARY: Identification of 7 genetic variants associated with protein consumption.
OVERVIEW: Proteins are essential macronutrients and building blocks of the body. More specifically, proteins are molecular machines that fulfill many functions inside and outside of cells. Proteins are made from 20 building blocks known as amino acids. While our bodies can make 11 of 20 amino acids, the remaining 9 must be consumed through the food we eat. On average, individuals consume approximately 7 grams of protein per 20 pounds of body weight per day. While protein is essential, excess protein consumption can result in metabolic disorders, such as obesity and diabetes. To identify genetic variants that may affect the amount of protein an individual consumes, this genome-wide association study examined the genomes of over 260,000 individuals of European ancestry. The study identified 7 genetic variants associated with protein consumption. The genetic predisposition to higher protein consumption was found to be correlated with obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and body mass index (BMI). The authors hypothesize that animal protein consumption, as opposed to plant protein consumption, is likely driving the positive correlation with poor health.
DID YOU KNOW? While there is conflicting research surrounding whether or not the consumption of red meat is harmful, most of the evidence supports high red meat consumption contributing to various health risks. Therefore, it is recommended to consume a maximum of two to three servings per week and supplement with other sources of protein, such as fish, eggs, nuts, and legumes. [SOURCE]
SAMPLE RESULTS: Learn more about the Nebula Research Library.
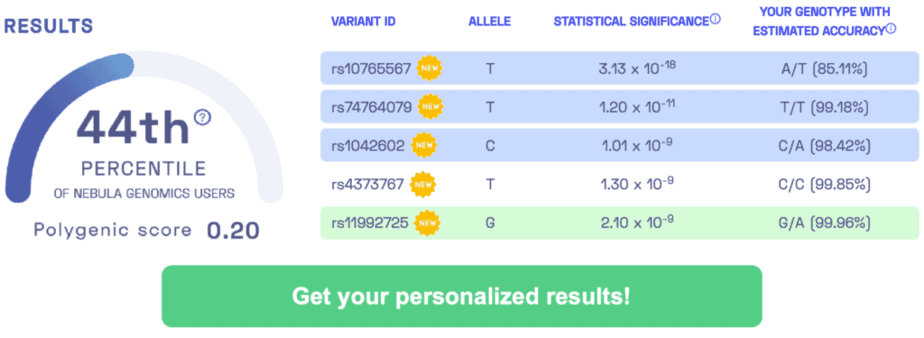
PROTEIN CONSUMPTION-ASSOCIATED VARIANTS: rs838133, rs13146907, rs1461729, rs1603978, rs55872725, rs780094, rs445551
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES:
What is protein?
Why do our bodies need protein? (Video)
YOU MAY ALSO BE INTERESTED IN:
Fat consumption (Meddens, 2020)
Sugar consumption (Meddens, 2020)
Carbohydrate consumption (Meddens, 2020)
Coffee consumption (Zhong, 2019)
Alcohol consumption (Evangelou, 2019)
WEEKLY UPDATE: May 26, 2020
