Table of contents
5 Facts About a Thyroid Test at Home
- Purpose: A thyroid test at home is suited for people who experience symptoms of hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, or have a history of thyroid problems or autoimmune disorders in their families. This test evaluates thyroid gland function by assessing levels of TSH, T3, T4, and, in some tests, thyroid antibodies.
- How it Works: When you visit the website, you order your thyroid test at home, which you usually get within 5 days. In all cases, you have to send a blood sample. The kit will include all the effects needed to do so at home.
- Cost: $69–$100
- Results: The testing company usually provides a card with information unique to you. Once the results are up, you will receive an email to check them online. If an abnormal level is detected, you might get a phone call from a nurse or medical advisor.
- Recommended product: Nebula 30X Whole Genome Sequencing is a reliable DNA Test that decodes all of your genetic blueprints with high accuracy
What is a Thyroid Test at Home?
A thyroid home health test provides a broad picture of the performance of the thyroid gland. Patients order a kit online, produce their blood samples with a finger prick and ship them back to the testing company, which will have certified labs to analyze them. This gland is located at the base of your neck and is responsible for producing hormones that regulate how your body uses energy. These hormones help regulate sleep, provide energy, and help keep you warm.
The thyroid gland regulates your metabolism by releasing triiodothyronine (T3) and tetraiodothyronine (T4). These are the main hormones secreted by this gland. A thyroid blood test at home measures the levels of these hormones in the blood.
When the body does not produce enough T3, T4, or both, you experience hypothyroidism. An estimated 5% of the population experience hypothyroidism, making it the most common thyroid issue. When these hormones are overexpressed, it leads to the opposite condition called hyperthyroidism. An estimated 1.2% of the population experience hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid nodules
They are small lumps in the thyroid gland. Most of them are non-cancerous, but their presence might indicate thyroid cancer. These nodules can also cause hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism
The most common symptoms of hypothyroidism are:
- Weight gain
- Dry skin
- Feeling cold
- Depression
- Fatigue or feeling tired at all times
- Slow heart rate
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Hair loss
- Muscle cramps
- Compromised memory
- Constipation
- Low sex drive
- Irregular periods
On the opposite end, hyperthyroidism occurs when there is an excess production of thyroid hormones by an overactive gland.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism include:
- Weight loss
- Anxiety
- Fatigue or feeling tired at all times
- Feeling hot and sweating all the time
- Thin and brittle hair
- Difficulty sleeping
- Muscle weakness
- Diarrhea
- Fast or irregular heart rate
- Tremors (in the hand, particularly)
- Goiter (enlarged gland)
- Low sex drive
- Irregular periods
Who can take a thyroid test at home?
Anyone can check their thyroid hormone levels, but generally speaking, asymptomatic patients do not need to take these tests. Generally, certain populations are at a higher risk of having compromising thyroid disorders:
- Women
- People older than 60
- People with autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes, Addison’s disease, and celiac disease
- People with a family history of thyroid condition
- Recently pregnant women
- Smokers
If you are experiencing symptoms of an interactive or underactive thyroid, you should consider taking an at-home test.
Biological markers
The home thyroid test measures four important biological markers when offering a thyroid test at home.
TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone)
This hormone is produced in the pituitary gland (located at the base of the brain) and is considered the most sensitive marker in a thyroid test. TSH controls the production of hormones by the thyroid gland. Therefore, comparing the levels of the thyroid-stimulating hormone with those of T4 and T3 can help determine a compromised thyroid or pituitary gland.
When thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels are too low, this means that your thyroid gland is producing too much T4, which leads to hyperthyroidism. Conversely, if the levels are too high, this indicates a lower production of T4, which can lead to hypothyroidism.
The changes in levels of T4 and T3 frequently happen during pregnancy and with the use of birth control pills.
FT4 (free thyroxine)
Thyroxine T4 is the most abundant thyroid hormone (over 90%). The levels of this hormone fluctuate in individuals having an underactive or overactive thyroid gland. Most T4 (and T3) circulates in the blood bound to a specific transport protein.
The free T4 (FT4) is not bound and can enter tissues and affect them. Hence, the importance of measuring those free hormones. A total T4 test would measure both, but it is the free T4 that provides more accurate results when compared with TSH levels.
A low TSH with an elevated FT4 is found when an individual has hyperthyroidism.
FT3 (free triiodothyronine)
Patients with hyperthyroidism will also display a large count of FT3. Triiodothyronine comprises less than 10% of the hormones produced by the thyroid gland. However, an individual can have low TSH and, as a consequence, high T3 but normal levels of T4.
Low levels of FT3 do not have the significant effect that low levels of FT4 would have, so they are not too helpful in determining hypothyroidism.
TPO (thyroid peroxidase antibodies)
TPO is a type of antibody that binds to thyroid enzymes and suppresses thyroid function. If a patient with hypothyroidism has elevated TPO, it is an indication of Hashimoto’s disease.
Other antibodies might be present and not tested for since they are not too common. For instance, the TSH receptor antibody (TSI) makes the thyroid gland overactive. This causes a disease known as Graves’ Disease. If your doctor detects this anomaly, they might order a thyrotropin receptor antibody test (TSHR) to see blocking and stimulating antibodies.
How Much Does a Thyroid Test at Home Cost?
Compared to other tests that entail more biomarkers, such as the at-home men’s health test or the at-home women’s health test, the price of this one is relatively low.
The biomarkers described above are the most commonly tested in most at-home thyroid tests. However, some companies might not test for TPO, while others might include other markers such as vitamin D and reverse T3.
- LetsGetChecked: $99 for the thyroid test (one-time purchase) or $119 for the thyroid antibody test (one-time purchase). There are subscription tiers per frequency:
- Every 3 months: $69.30/$83.30 (30% off the one-time purchase price)
- Every 6 months: $79.20/$95.20 (20% off the one-time purchase price)
- Every 12 months: $84.15/$101.15 (15% off the one-time purchase price)
- EverlyWell: $99. You may also become a “Control member” for a monthly $24.99 subscription and get one test per month. Their at-home thyroid test is included in this subscription.
- Paloma Health: $99
- Imaware: $69. This one is for females only and only a TSH test
Getting Started with a Thyroid Test at Home
To order a thyroid test at home, you must visit the testing company website and order from there. Once the order is complete, you should get a kit at your doorstep within 5–7 days. The first thing that you need to do is to find an ID or activation code so that the company can link you to your sample once they process it at their labs.

For this test, you will need to send a blood sample. Some companies will ship a blood collection tube with heparin, while others will send a card with five circles to stain with blood. In the latter case, samples are dry blood.
All kits normally contain:
- Instructions sheet
- Patient ID card (keep that with you)
- Return envelope with a prepaid shipping label
- Biohazard bag
- Lancets (2 or 3)
- Blood collection tube or card (for dry samples)
- Alcohol swabs or wipes
- Bandages
To consider before taking this test:
- You must take the blood sample early in the morning (usually before 9 am).
- No fasting is needed, although eating a considerable amount of food might affect TSH levels.
- Send your results as soon as possible – preferably the same day you took the blood sample.
- Drink water before taking the test.
- It is a good idea to wash your hands with warm water to improve circulation.
Thyroid Test at Home Test Results
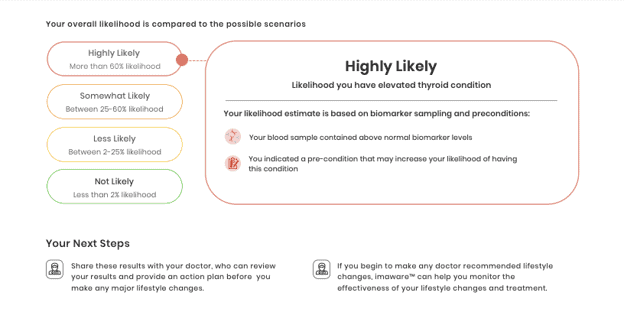
When your samples arrive at the testing company, a medical professional reviews and analyzes the results. Your values are compared against a reference range. Usually, you will receive detailed information of your thyroid function test that describes whether your biomarkers appear elevated, normal, or low. If there is any abnormality, they might give you a call, and perhaps your next course of action would be to visit a physician.
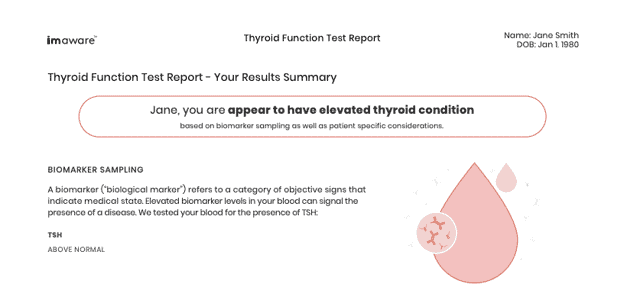
Most of the home test kits will include interpretation of the results. If not, it is always best to consult your physician.
Results are as accurate as lab tests. Share your results with your physician on your next visit so that they can help you establish changes in your lifestyle or medication.
Your doctor may order additional tests if any level abnormalities are found. These may include an ultrasound test and thyroid uptake tests to look for any structural problem with the thyroid gland, activity, or tumors that may be causing it to underperform. Based on the results, the doctor may prescribe a sample tissue to check for thyroid cancer.
Most testing companies would recommend taking this test every six months. However, if there has been a change in medication, an 8-week time between them is best.
Note that most insurance companies will not cover the costs of these at-home tests. However, the cost is usually lower than visiting a lab and getting results and analysis. Get in touch with your insurance company to discuss coverage.
You may also be interested in these other wellness tests you can take from home:
- Women’s health test (hormones, cholesterol, nutrients, and more)
- Men’s health test (hormones, proteins, cholesterol, and more)
- Heart health test (cholesterol and other lipids)
- Inflammation test (CRP, vitamin D, Procalcitonin, and more)
- Vitamin D test (hydroxyvitamin D levels)
- Cholesterol test (total cholesterol, HDL, LDL, and triglycerides)
- Testosterone test (total, free, SHGB binding, albumin binding)
- Metabolism test (testosterone, TSH, cortisol, and progesterone)
- Food sensitivity test (immune response to up to 600 foods)
Edited by Christina Swords, PhD
