Table of Contents
5 Facts about at-home Women’s Health Tests
- Purpose: measures the levels of a certain number of hormones so that patients can address health issues related to abnormal amounts. They have the same accuracy as traditional lab tests. In most products, the number of biomarkers tested ranges from 7–11.
- How it Works: Order online, and receive a kit in 5–7 days with instructions, collection material, and a pre-paid return envelope. Perform the tests, send them back to the lab, and within days or weeks, you will get your results online.
- Cost: Varies. Prices usually range between $85–$299.
- Results: Results include levels for the markers offered and whether they fall within the normal range. If any values are abnormal, the company provides advice on how to improve them. The company will usually suggest retaking the test after some period.
- Recommended products: Nebula 30X Whole Genome Sequencing is a reliable DNA Test that decodes all of your genetic blueprints with high accuracy
What is an At Home Women’s Health Test?
An at-home women’s health test refers to comprehensive health screenings to determine some biomarkers levels. The test helps detect imbalances that cause certain symptoms affecting the patient’s general health.

Hormones
Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate body functions. For them to work correctly, they must be at an optimal level. Hormonal imbalances occur when the body produces too much or too little of a particular hormone. When this occurs, women may experience specific health problems or an overall decrease in well-being.
Hormone levels are an essential component of women’s health. Abnormal hormone levels may cause:
- Gain weight or loss with no apparent cause
- Unusual cold and heat sensitivity
- Skin rashes
- Excessive or unexplained sweating
- Sleep difficulties
- Abnormal heart rate
- Changes in blood pressure
- Weak bones
- Changes in blood sugar concentration
- Extreme fatigue with no cause
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Depression
- Headaches and migraines
- Excessive thirst
- Appetite changes
- Bloating
- More frequent trips to the bathroom
- Puffy face
- Neck bulge
- Blurred vision
- Tenderness on the breasts
- Low libido
- Infertility
- Changes in the menstrual cycle
Products such as Viviscal and Nutrafol for hair growth and Leptitox for weight loss, contain ingredients aimed at reducing or increasing the production of hormones.
An at-home women’s health screening test will help you determine the type and extent of an imbalance, if present. With this information, patients and their health care providers can discuss more targeted and effective treatments.
The following is a list of the most common biomarkers tested with an at-home women’s health test. The number and types of markers will vary, and no comprehensive kit tests for all of them.
Progesterone: Progesterone is an important reproductive hormone necessary to maintain a pregnancy. It also helps hold the endometrium. This hormone stops its production when ovulation ceases during menopause.
Low progesterone symptoms include:
- Hot flashes
- Headaches or migraines
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Mood changes
- Low libido
- Irregular periods
- Absence of periods
Free testosterone: Testosterone is produced in the adrenal glands and the ovaries. It is a sex hormone important for sex drive, mood, muscle and bone health, and cognitive function. It is important to point out that this test measures only testosterone navigating freely in your bloodstream and not your total testosterone.
Some studies have shown that high exposure or high levels of progesterone, testosterone, and estrogens are linked to an increased risk of breast cancer.
Estradiol: Estradiol is one of the principal sex hormones responsible for ovulation. This estrogen is also responsible for the normal function and health of sexual organs.
Luteinizing hormone: Released by the pituitary gland (located at the base of the brain), this hormone triggers ovulation. An average hormone level during the second half of the menstrual cycle indicates normal ovary function.
Follicle-stimulating hormone: As its name indicates, FSH is the hormone responsible for the maturation of the follicle, which will release estrogen and progesterone. It is also produced in the pituitary gland. Normal levels indicate that a woman has a regular count of eggs.
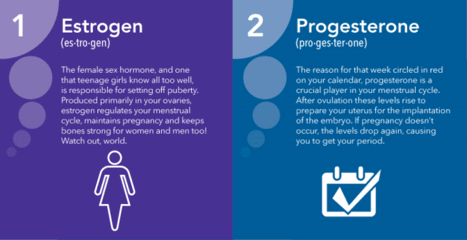
Cortisol: Cortisol is the hormone we need to manage stress. Throughout the day, it fuels us by stimulating the release of glucose. Since we are at different energy levels and stressors might vary throughout the day, kits with this test will require several samples at different times.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone: Another hormone secreted by the pituitary gland, TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to release thyroid hormone into the bloodstream. There are numerous health conditions that may be detected through the levels of TSH.
Triiodo-thyronine (T3): This hormone produced by the thyroid gland controls thyroid function, which in turn controls metabolism. At-home tests measure the amount of T3 that is freely floating in the blood (free T3).
Free thyroxine (T4): This is the principal hormone released by the thyroid gland. It plays a vital role in heart and muscle function, digestion, bone maintenance, and brain development. This test is recommended if you have signs of a thyroid disorder.
Some symptoms associated with a deficiency of free T4 include hypopituitarism (low production of hormones by the pituitary gland), enlarged thyroid gland, nodules or lumps in the thyroid, and pregnancy issues.
DHEAS: DHEAS (dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate) is involved in the production of other hormones such as estrogen and testosterone. It is an androgen hormone produced by the adrenal glands and ovaries. This hormone also helps control the harmful effects of high cortisol levels.
High levels of DHEAS may indicate:
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia: a common congenital disorder of the adrenal glands. This is a tumor that can be benign or cancerous.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome: an endocrine disorder that happens at any age after puberty. Common symptoms include weight gain, excessive facial and body hair, infertility, irregular menstrual periods, and increased risk of heart disease and diabetes.
- Body changes of a girl in puberty happening earlier than they should.
On the other hand, low DHEAS levels may indicate:
- Hypopituitarism
- Addison’s disease: also called adrenal insufficiency, this condition causes a low production of cortisol and aldosterone by your adrenal glands.
SHBG: SHBG (sex hormone-binding globulin), as its name suggests, binds to certain hormones and transports them through the bloodstream. While bonded to SHBG, your body cannot use these hormones. This helps regulate the amount that your body may use. An imbalance of this hormone usually results in low levels of estradiol and testosterone.
Cholesterol
Cholesterol building up in arteries is a major cause of heart disease. This is why some tests include markers that are risk factors. This lipid panel for heart health includes:
Total cholesterol: Some tests will include a measurement of your cholesterol levels. This lipid will determine your risk for a heart attack and other blood vessel conditions. A total cholesterol test will calculate the four types of fats in your blood: Total cholesterol, HDL (high-density lipoprotein), LDL (low-density lipoprotein), and triglycerides.
HDL: This is known as the “good cholesterol” because it absorbs cholesterol and sends it back to the liver, where it is flushed out from the body. HDL’s main role is to keep your arteries clear. High levels of this lipoprotein reduce your risk of a heart attack.

LDL: This is the bad one. An excess of this lipoprotein will cause a buildup of plaque (fatty deposits) in your arteries, compromising your blood flow. Sometimes, these plaques may rupture, causing a heart attack.
Triglycerides: When you eat more than what you need, your body converts excess calories into triglycerides and deposits them in fat cells. This type of cholesterol is associated with being overweight, poor eating habits, smoking, sedentarism, or diabetes.
Other nutrients
Some at-home women’s health tests will ensure proper overall health and determine other substances such as sugar (glucose), vitamins, and enzymes. These tests may include:
HbA1c: The Hemoglobin A1c test is an indicator of average blood sugar for the past 2 to 3 months. Namely, it measures the amount of sugar (glucose) attached to hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a molecule in your red blood cells in charge of carrying oxygen and other nutrients to the organs in your body.
Vitamin D: Vitamin D is an essential nutrient for healthy bones and teeth. There are two types of vitamin D necessary for health and nutrition: vitamin D2 and vitamin D3. These two change into a form of vitamin D called 25 hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) in the bloodstream. This test measures the amount of 25(OH)D in your blood.
Mostly, this test monitors bone disorders as these would be caused by a vitamin D deficiency.
Thyroid peroxidase (TPO) antibody: Some at-home women’s health tests also screen for this antibody. TPO is an enzyme found in the thyroid gland and is important for the production of thyroid hormones. This test detects the presence of antibodies that would halter TPO production, producing hypothyroidism, whose effects we have already discussed.
An elevated count of these antibodies causes a condition known as Hashimoto’s disease, the most common type of hypothyroidism in the United States.
How Much Does an At home Women’s Health Test Cost?
If you are planning on taking a test, you will find that prices will vary depending on the company selling it. Also, you must consider that some tests are more thorough than others. Overall, these are the prices for some tests out there:
EverlyWell: $199, but you get a discount if you subscribe, meaning that you decide how frequently you will take the test. Taking these tests at certain intervals allows you to monitor abnormalities.
- Semi-annual subscription (a kit every six months): $169 (15% off regular price)
- Quarterly subscription (a kit every three months): $159 (20% off regular price)
- Monthly subscription (a kit every month): $149 (25% off regular price)

myLABBOX: $299
Imaware: $149
Some companies sell each at-home test individually, each one costing $80–100.
Getting Started with an At Home Women’s Health Test
The first step to getting tested is to go to your preferred site and order the test kit. Your package will arrive within 3–5 days. It slightly varies among companies, but most of the kits include:
- Directions
- Pre-paid shipping label
- An activation card
- Medical grade collection device or card (for blood samples)
- Saliva tubes (for tests that also require saliva sample collection)
- Lancets (for finger pricking)
- Alcohol pads
- Gauze
- Bandage
The next step is to register your test kit online (you will receive a code). This will allow you to receive updates about shipping and test results.
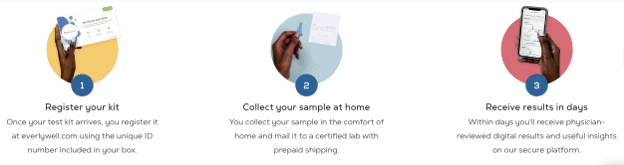
It is important to note that you must take the test on certain days of your cycle. The directions will indicate the best days to perform the tests – typically on the third day of menstruation.
The optimal time to take the test is in the morning, usually around 30 minutes after getting up. For kits involving blood and saliva samples, dried blood works perfectly, and you can freeze your saliva samples until you are ready to ship them.
In preparation for the test, the following are some recommendations before taking it:
- Temporarily stop taking any medications that would affect the results, especially medicines containing hormones or hormone stimulants such as estrogen, anti-seizure drugs, glucocorticoids, prednisone, prednisolone, and hydrocortisone. Never suspend or change the use of any medication without consulting with your health provider first.
- You should not be using any hormonal contraception. If you were on hormonal birth control, wait at least three months after suspending it before taking the test to give your cycle time to return to normal. Some companies recommend waiting a year if you are using a contraceptive injection.
- Some tests warn against taking the test if you are breastfeeding since it will be more difficult to interpret your results.
- Do not take this test if you are pregnant.
- In most cases, you will need to fast for at least 8 hours before taking the test.
After you have collected your samples, return them to the lab, and within days, you will receive an email indicating that you can access your results online.
At Home Women’s Health Test Results
A test result is comprehensive and, in addition to the levels of each of the biomarkers, it will include a comparison range for each one, recommendations based on the values, and next steps.
When deciding what at-home women’s health test to take, make sure that a certified doctor reviews the results. This will ensure the validation of your product. At-home tests have the same accuracy as traditional blood tests and are backed up by medical professionals.
After getting your results, take them to your health provider to devise a plan to help you achieve your medical goals. Most tests include clear information intended to inform you as the patient, but more thorough ones will also include information intended for your doctor to interpret your results better.
In addition to these at home panels, it is important that women ages 25 and older also get routine cervical cancer screenings provided by their health care provider. HPV screening is recommended every 5 years and Pap smears are recommended every 3 years. Women over the age 45 should get breast cancer screening annually.
Women’s health tests for sexual health, such as screening for chlamydia and gonorrhea, are available from at home companies and through a medical provider.
You may also be interested in these other wellness tests you can take from home:
- Men’s health test (hormones, proteins, cholesterol, and more)
- Heart health test (cholesterol and other lipids)
- Inflammation test (CRP, vitamin D, Procalcitonin, and more)
- Vitamin D test (hydroxyvitamin D levels)
- Cholesterol test (total cholesterol, HDL, LDL, and triglycerides)
- Thyroid test (TSH, FT4, FT3, and TPO)
- Testosterone test (total, free, SHGB binding, albumin binding)
- Metabolism test (testosterone, TSH, cortisol, and progesterone)
- Food sensitivity test (immune response to up to 600 foods)
Edited by Christina M. Swords, PhD
